Campylobacter is a bacterium responsible for campylobacteriosis. The infectious ailment causes vomiting, diarrhea, fever and cramping. The condition generally spreads via contaminated water and food. Both animals and humans can become infected if exposed to the feces of infected animals such as cattle, chickens and household animals. The condition also spreads if infected meat was not properly cooked as well as from contaminated water sources and unpasteurized milk.
The infection usually affects the elderly and individuals with weakened immune systems. If the bacteria move into the bloodstream, it can become dangerous.
What are the indications?
The indications of a campylobacter infection generally manifest in 1-7 days after exposure to the bacteria such as:
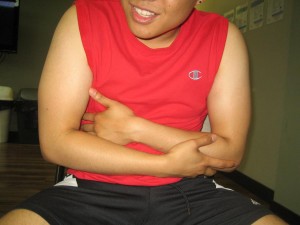
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Headache
- Low abdominal pain
- Diarrhea that might contain blood or mucus
- Stomach cramps
The symptoms can last for up to a week while some do not have any symptoms at all.
Preventive measures
- Always wash hands thoroughly before handling food especially the raw ones
- Prevent cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards for vegetables and meat
- Clean countertops and utensils with hot soapy water after contact with raw meat
- Avoid unpasteurized milk
- Chicken meat must be cooked thoroughly until there are no pink parts
- Do not drink water from streams particularly those that flow through areas where animals reside
- Toilets must be disinfected after used by an individual with diarrhea
Management of campylobacter infection
Generally, there is no specific treatment for campylobacter infection. In case dehydration occurs, it is usually due to diarrhea. It is vital to increase the intake of fluids.
Antibiotics such as erythromycin and azithromycin are prescribed by the doctor to minimize the symptoms if the infection is detected early.
