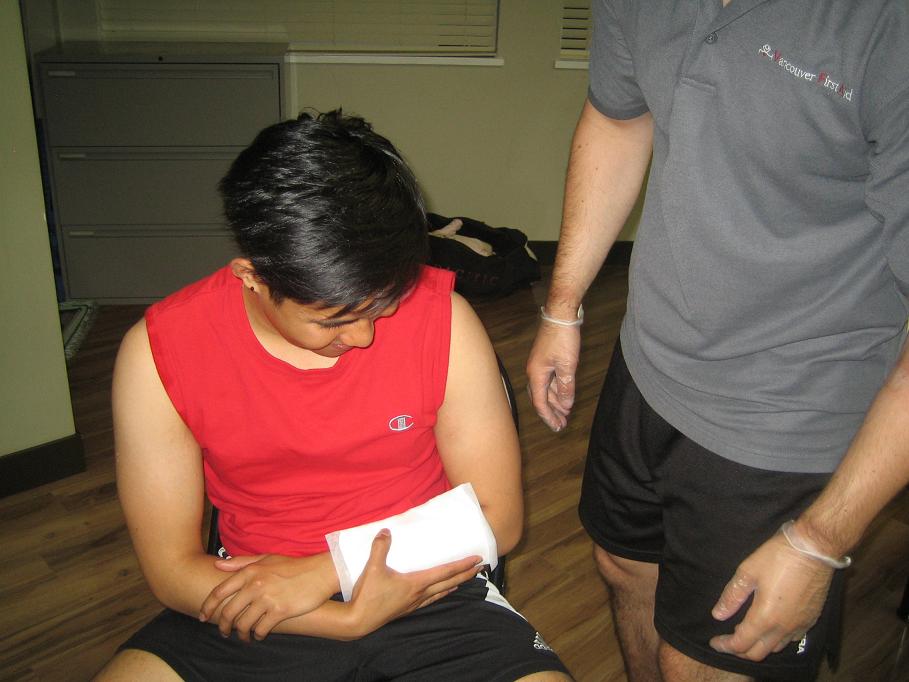
Chemical burns can be painful but most are not serious. The typical causes of chemical burns include drain cleaners, tile cleaners, gasoline, car battery acid, oxidizers and wet or dry cement. When an individual sustains a chemical burn, it is important to ensure proper treatment to promote healing of the skin.
Removing contact
If an individual ends up with a chemical burn, the cause must be removed. If caused by a dry chemical, you should brush off any remaining substance on the skin.
Rinse the skin under cool running water for at least 20 minutes. Get rid of any contaminated jewelry or clothing to prevent contact with the skin.
Wound protection
After the burn site is rinsed with cool water, it should be wrapped loosely using cloth or sterile dressing. Make sure that the area is protected from friction or pressure and avoid disturbing blisters or extract the dead skin from the burn.
For minor chemical burns, it usually heals on its own without requiring further treatment.
Pain relief for chemical burns
One way to relieve the pain from chemical burns is to apply a cool, moist compress on the area. The individual can also be given an over-the-counter pain medication or one prescribed by the doctor.
Considerations
It is best to seek immediate care if shock occurs such as shallow breathing or fainting after a chemical burn. Remember that chemical burns that penetrate the first skin layer or on the hands, eyes, face, feet, buttocks, groin or over a major joint or wide area in the body must be treated by a doctor.
For chemical burns, tetanus shots might be considered. Take note that burns are susceptible to tetanus.
Disclaimer / More Information
The information posted on this page on chemical burns is for learning and educational purposes only. To learn to properly deal with burns including chemical burns, register for first aid training at one of our training centers located throughout Canada. The training centers are in Edmonton, Calgary, Vancouver, Kelowna, Surrey, Winnipeg, Toronto, Ottawa and Halifax.